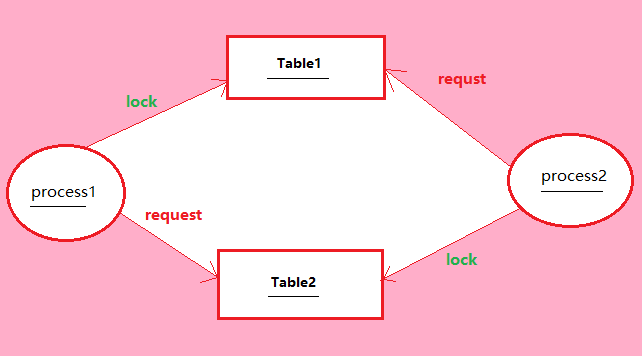
What's Deadlock in SQL Server?
- Deadlock occurs when two or more transaction block each other by holding lock the resource each of the transaction also needs
- When deadlocks occur, SQL Server will choose one of the processes as the deadlock victim and rollback that process, so the other process can move forward.
- The transaction that is chosen as the deadlock victim will produce an error.
How SQL Server detects deadlocks:
There is a Lock Monitor Thread runs every 5 seconds to detect any deadlock.
What is DEADLOCK_PRIORITY?
By default, SQL Server chooses a transaction as the deadlock victim that is least expensive to roll back.
you can specify the priority of the session using this statement
SET DEADLOCK_PRIORITY NORMAL
- The default is Normal
- Can be set to LOW, NORMAL, or HIGH
- Can also be set to a integer value in the range of -10 to 10.
LOW : -5
NORMAL : 0
HIGH : 5
In your example :
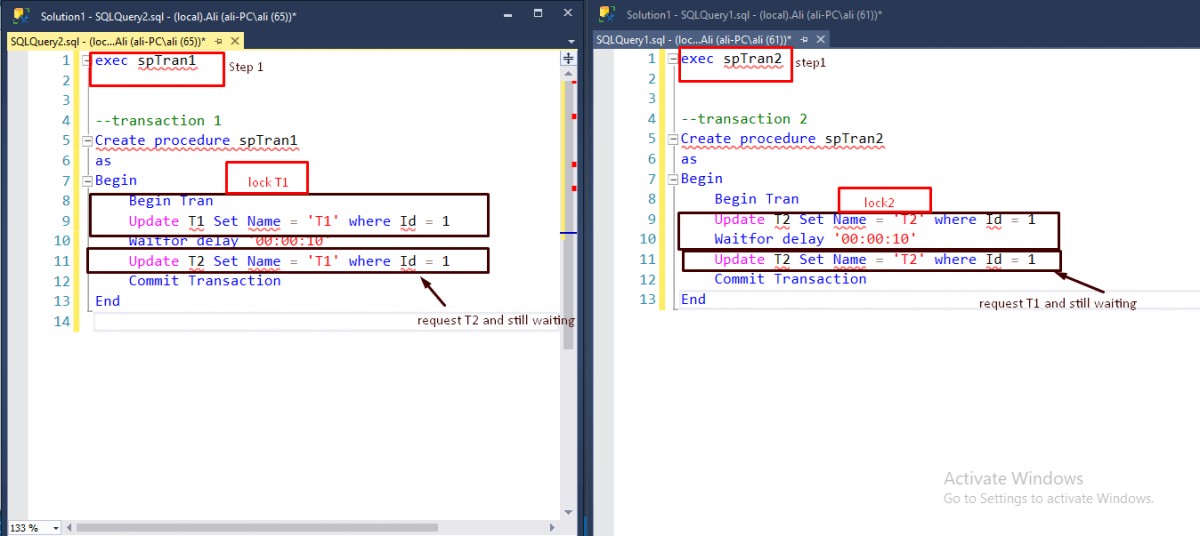
You created two stored procedure that contains two transactions. Execute spTran1 in the session of SQL and then execute spTran2 in another session Transaction1 will lock Table1 and wait for 10 seconds and in another session of SQL server Transaction2 to lock Table2 and wait 10 second after 10-second the SQL server want to complete spTran1 so request Tabl2 in transaction1 and then it is waiting, and in another session doing the same thing want to request table1 in transaction2 and it is waiting after a few second ones of the transaction complete successfully and another transaction is deadlock victim
If you want to solve this problem you need to ensure that Table1 & Table2 are accessed in the same order every time.
-- Transaction 1
Create procedure spTran1
as
Begin
Begin Transaction
Update Table1 Set Name = 'Trans1' where Id = 1
Update Table2 Set Name = 'Trans1' where Id = 1
Commit Transaction
END
-- Transaction 2
Create procedure spTran2
as
Begin
Begin Transaction
Update Table1 Set Name = 'Trans2' where Id = 1
Update Table2 Set Name = 'Trans2' where Id = 1
Commit Transaction
END
The following picture explains this